Modern Chemistry Textbook Chapter 16 Chapter Review Answers Pdf
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemical science Chapter 16 – Costless PDF Download
*According to the latest update on the term-wise CBSE Syllabus 2021-22, this chapter has been removed.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life is the all-time study material that tin assist you to score good marks in the CBSE Class 12 examination. The NCERT Solutions for Course 12 Chemistry gives you precise answers to the textbook questions, MCQs, HOTS (Higher Lodge Thinking Skills), worksheets, exercises and assignments.
To primary Class 12 Chemistry one must solve the questions provided at the end of each chapter. Solving these questions with the help ofNCERT Solutions for Form 12 Chemistry is the best mode. These solutions are framed in a simple stepwise way for improve understanding. Admission the free PDF of the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemical science for this chapter from the link attached beneath.
Download NCERT Solutions Form 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 PDF:-Download Here
Grade 12 Chemical science NCERT Solutions Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life – Important Questions
Question 1:
Why practice nosotros need to classify drugs in dissimilar ways ?
Answer :
The reason for the drug'southward classification is as follows:
(i) The pharmacological impact is based on:
To physicians this definition is helpful. Information technology provides a whole array of drugs to classify drugs to different diseases.
(two) Based on activity on the drugs:
This is based on a drug'southward action on a specific biochemical process.
(iii) Edifice on chemical structure:
The range of drugs that share mutual structural characteristics and have similar pharmacological activity.
(iv) Building on molecular objectives:
Many medications accept the same action office on targets. In such cases this distinction is useful.
Question 2:
Explain the term, target molecules or drug targets as used in medicinal chemistry.
Answer
The drug targets are the primal molecule responsible for some metabolic pathways that tin cause specific diseases. The drug targets are proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids.
Chemical agents used to block those target molecules are called drugs by fusing with the active sites of cardinal molecules.
Question 3:
Proper name the macromolecules that are chosen as drug targets.
Answer
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids are the macromolecules selected equally targets for the drugs.
Question 4:
Why should medicines not be taken without consulting doctors?
Answer
Medicines should not be taken without consulting a doctor because it can bind to more than than ane receptor site. Thus it tin can be harmful to some receptor sites. Medicines, when taken in higher doses, can cause harmful effects. And then medicines tin be poisonous.
Question 5:
Define the term chemotherapy.
Answer
Chemotherapy is the apply of chemicals for medicinal effects. Sources are the use of chemical agents for disease prevention, diagnosis and treatment.
Question half-dozen:
Which forces are involved in holding the drugs to the active site of enzymes ?
Answer
The forces responsible are
(1) Hydrogen bonding
(ii) Ionic bonding
(3) van der Waals strength
(4) Dipole-dipole interaction
Question vii:
While antacids and antiallergic drugs interfere with the function of histamines, why practice these non interfere with the function of each other ?
Respond
Sure drugs merely bear upon specific receptors. Antacids and antiallergic drugs do non interfere, as they work on different receptors. That is why antacids and antiallergic drugs interfere with histamine function but not with each other.
Question 8:
Depression level of noradrenaline is the cause of low. What type of drugs are needed to cure this problem ? Proper noun two drugs.
Answer
Antidepressant drugs are used to lessen the depression effect. These drugs contain enzymes that catalyze the degradation of the neurotransmitter, noradrenaline. The neurotransmitter is therefore slowly metabolized and can activate the receptor for a longer period of fourth dimension.
The two anti-depressant drugs are:
ane. Phenelzine
ii. Iproniazid
Question 9:
What is meant by the term 'broad spectrum antibiotics' ? Explain.
Reply
Antibiotics are known as wide-spectrum antibiotics, which are effective against a wide range of gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. Eg: Chloramphenicol
This is used to treat astute fever, typhoid, meningitis, dysentery, tuberculosis and certain types of urinary tract infection. The other 2 broad-spectrum antibiotics are vancomycin and ofloxacin. Amoxicillin and ampicillin −synthetically derived from penicillin-, are also antibiotics of wide-spectrum.
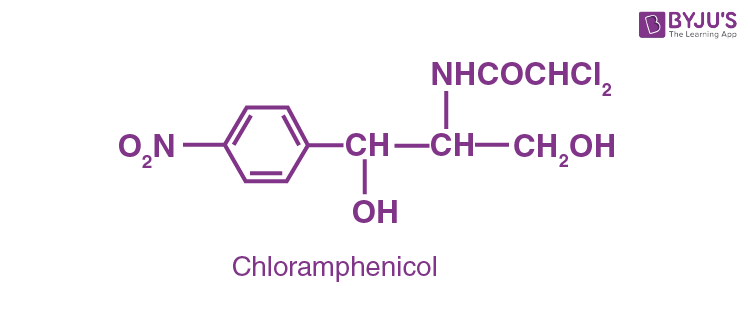
Question 10:
How do antiseptics differ from disinfectants? Requite one case of each.
A nswer
Disinfectants and antiseptics against micro-organisms are actually successful. Antiseptics are used to treat living tissues such equally cuttings, wounds, diseased skin surfaces and ulcers, while disinfectants are used for objects such equally floors, drainage systems, instruments, etc. Disinfectants damage living tissues.
Iodine is a potent antiseptic. The iodine tincture is applied to wounds. I percentage phenol solution is used as a disinfectant.
Question 11:
Why are cimetidine and ranitidine better antacids than sodium hydrogencarbonate or magnesium or aluminium hydroxide?
Answer
The antacids that neutralize backlog muriatic acid in the stomach are magnesium hydroxide, sodium hydrogen carbonate, and aluminium hydroxide. Nevertheless, the motive for releasing excess acid remains untreated.
Cimetidine and ranitidine are good antacids because they control the acidity cause.These drugs preclude histamine from interacting with the receptors with the present in the walls of the stomach, and can, therefore, reduce the amount of acid released past the stomach.
Question 12:
Name a substance which can be used as an antiseptic as well as a disinfectant.
Answer
Phenol is the substance which tin can be used as an antiseptic and equally a disinfectant. 0.ii percent phenol solution can exist used as an clarified and one pct of the solution should exist used for disinfectant.
Question 13:
What are the main constituents of Dettol?
Respond
Dettol's principal constituents are chloroxylenol and
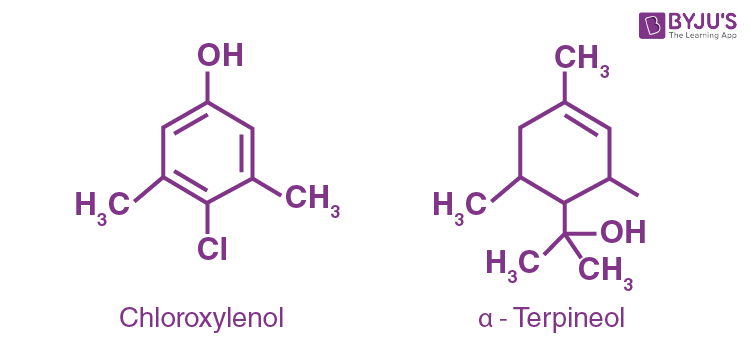
Question fourteen:
What is tincture of iodine ? What is its use ?
Answer
For alcohol-water mixtures, 2-iii percent of iodine is referred to as iodine tincture and is primarily added to wounds.
Question 15:
What are food preservatives ?
Answer
Chemicals that prevent microbial growth are referred to as preservatives for food. They cut back on spoilage. Some food preservatives are saccharide, table salt, vegetable oil, propanoic acid salts and sodium benzoate(C6H5COONa).
Question 16:
Why is utilize of aspartame limited to cold foods and drinks ?
Respond
Aspartame is not stable at cooking temperature and therefore their use is limited only to cold foods and beverages.
Question 17:
What are artificial sweetening agents ? Give two examples.
Answer
Those chemicals which sweeten nutrient are called artificial sweeteners. Bogus sweeteners don't add calories to our bodies and don't injure the homo body, either. Some known artificial sweeteners are sucralose, aspartame, alitame, and saccharin.
Question xviii:
Name the sweetening agent used in the preparation of sweets for a diabetic patient.
Answer
Saccharin, aspartame and alitame are sweetening agents used to set sweets for patients with diabetes.
Question 19:
What problem arises in using alitame as artificial sweetener ?
Answer
Alitame is a sweetener of nifty authorization. The sweetness of the food while using alitame as an artificial sweetener is difficult to control.
Question 20:
How are constructed detergents better than soaps ?
Reply
Constructed detergents are used in both soft h2o and difficult water, while soaps are used in soft h2o. In hard water, soaps aren't constructive. The synthetic detergents are therefore better than the soaps.
Question 21 :
Explicate the following terms with suitable examples
(i) cationic detergents
(ii) anionic detergents and
(iii) not-ionic detergents.
Answer
(i) Cationic detergents
Cationic detergents are commonly called 4th ammonium salts of acetates, chlorides, or bromides.
Cationic detergents are named equally such because the cationic role of the aforementioned chemical compound detergents has an extended hydrocarbon concatenation and a positive charge on the N cantlet.
eg : cetyltrimethylammonium bromide
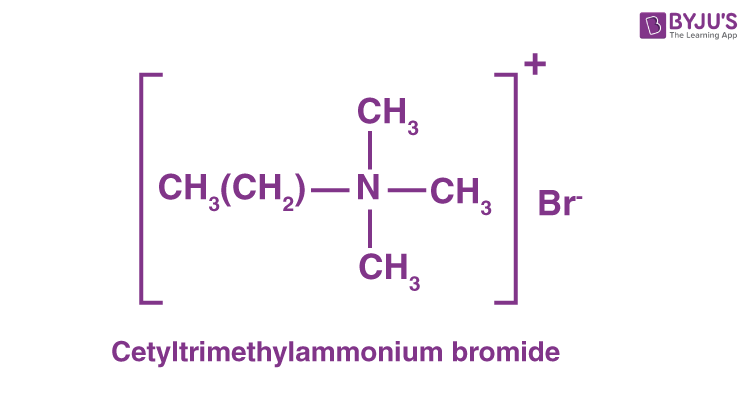
(ii) Anionic detergents
Type of anionic detergents are equally follows:
1. Sodium alkyl sulfate detergents are simply long-chain sodium alcohol salts. They are made past using concentrated sulphuric acid to react to such booze and afterward by sodium hydroxide.
Examples of such detergents include sodium lauryl sulfate (
2. Sodium alkylbenzenesulphonates: Sodium salts of long-chain alkylbenzenesulphonic acids are such detergents. These are synthesized by benzene alkylation by Friedel-Crafts along with alkyl halides or alkenes with long chains. The resulting product initially reacts with full-bodied sulphuric acid and after reacts with sodium hydroxide. Sodium 4-(ane-dodecy) benzenesulfonate is an case of anionic detergents.
(iii) Not-ionic detergents
There are no ions in molecules of those detergents. They are a good case of high-molecular-mass booze esters. These are prepared by the stearic acrid and polyethylene glycol reactions.
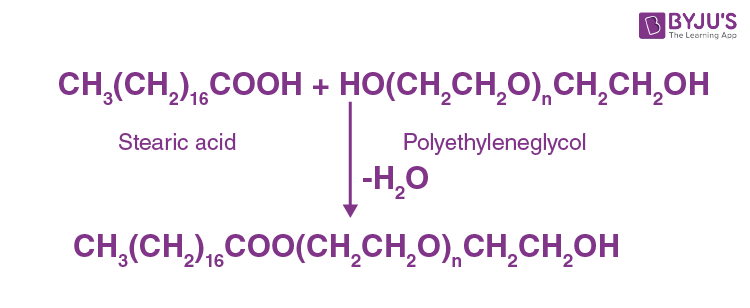
Question 22:
What are biodegradable and non-biodegradable detergents ? Give one case of each.
Answer
Biodegradable detergents are Leaner degrading detergents. They do have straight chains of hydrocarbons. Sodium lauryl sulfate for case.
The non-biodegradable detergents are detergents that bacteria tin can not degrade.Their hydrocarbon chains are strongly branched.
For case: benzene sulphonate with sodium -iv- (1, iii, 5, 7- tetramethyl octyl)
Question 23:
Why do soaps not work in difficult water ?
Respond
Sodium or potassium salts with long-concatenation fatty acids are nowadays in soaps. Difficult water contains magnesium and calcium. When the ions displace sodium or potassium on dissolving soaps in hard water, insoluble calcium or magnesium salts of fatty acids course. Separate those insoluble salts as scum.
This is why soaps aren't working in harsh water.
Question 24:
Can yous use soaps and synthetic detergents to check the hardness of water ?
Answer
Soaps will precipitate in difficult water but in soft h2o, it volition not become precipitated and can, therefore, be used to find the water'due south hardness. On the other hand, synthetic detergents won't get precipitated in both hard water and soft water and can't be used to find water hardness.
Question 25:
Explain the cleansing activeness of soaps.
Respond
Soap molecules class micelles around an oil droplet (drit) in such a way as to attach the hydrophobic parts of the stearate ions to the oil droppler and project the hydrophilic parts outside the oil droplet. The stearate ions (along with the dirt) are pulled into the water because of the polar nature of the hydrophilic parts, thereby removing the dirt from the cloth.

Question 26:
If water contains dissolved calcium hydrogencarbonate, out of soaps and synthetic detergents which one will you utilise for cleaning apparel ?
Answer
Synthetic detergents are commonly used for apparel washing. Such ions form insoluble salts when dissolved in water containing calcium ions which are of no use. Constructed detergents are dissolved in calcium ion-containing h2o, such ions class soluble salts which act as cleaning agents.
Question 27:
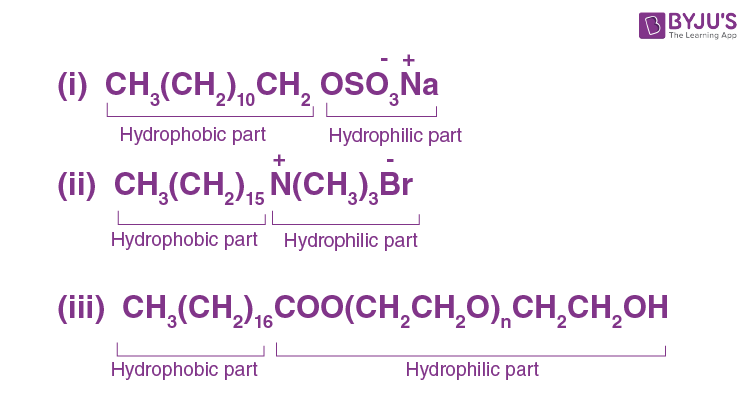
Characterization the hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts in the following compounds.
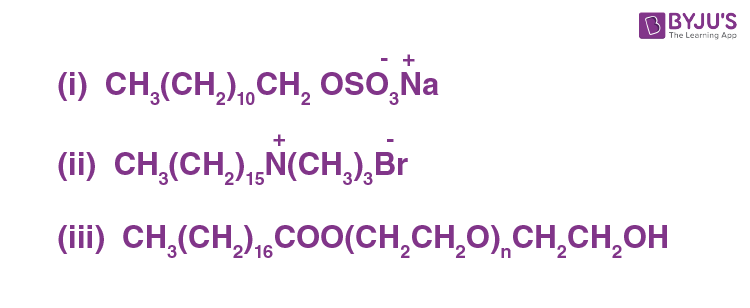
Answer

Chemistry influences every sphere of human life and the principles of chemistry take been used for the benefit of mankind. Chemistry in everyday life questions and answers pdf are prepared by experienced teachers as per the latest CBSE syllabus. Students must practice the NCERT Solutions for Form 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 regularly to excel in their lath exam.
Class 12 NCERT Solutions for Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life
Grade 12 Chemistry Chapter sixteen includes the topic – Drugs and their classifications:
- Drug Target Interaction: Enzymes as drug targets, Receptors as drug targets.
- Therapeutic Action of different classes of drugs: Antacids, Antihistamines, Neurologically Active Drugs, Antimicrobials, Antifertility Drugs.
- Chemicals in food: Artificial Sweetening Agents, Food Preservatives.
- Cleansing Agents: Soaps, Synthetic Detergents.
The near abundant metallic plant in the globe'due south crust is Aluminium which is Approx 8.3% by weight. Cleaning of ore or removal of particles like sand, clay from the ore is called dressing of ore or concentration of ore. This is done in the following steps: Hydraulic washing, magnetic separation, froth floatation method, leaching. This was brief on Chemistry in everyday life and tin can exist well comprehended with the help of NCERT Solutions for Class 12. Pupil must too solve the exemplary questions of this chapter to attain a house grip over the ket concepts.
Subtopics of Class 12 Chemistry Affiliate sixteen – Chemical science in Everyday Life
- Drugs and their Classification
- Drug-Target Interaction
- Therapeutic Activeness of Different Classes of Drugs
- Chemicals in Food
- Cleansing Agents
Why Opt for BYJU'South?
Chemical science is a tough subject area for many students and they always struggle to remember the concepts, derivations, chemical and structural formula. BYJU'S videos guide you in remembering the concepts and assignments provided by the states, which will help you in practising important derivations, numerical problems, and structural formulas.
Apart from NCERT Solutions Grade 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 – Chemistry in Everyday Life, students can admission other NCERT Solutions for other chapters every bit well. Students can download worksheets, assignments, NCERT Course 12 Chemistry pdf, and other study materials for exam preparation and to score better marks.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16
Which topics are important in the Chapter 16 of NCERT Solutions for Course 12 Chemical science?
The topics of import in the Chapter 16 of NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry are –
1. Drugs and their Classification
two. Drug-Target Interaction
three. Therapeutic Action of Dissimilar Classes of Drugs
four. Chemicals in Food
five. Cleansing Agents
What questions can I expect from the Chapter 16 of NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry?
The questions which you can expect from the Affiliate 16 of NCERT Solutions for Form 12 Chemistry are –
i. Explain the term broad spectrum antibiotics.
two. What is the tincture of iodine and explicate its uses?
3. Which substance tin can be used as both antiseptic and disinfectant?
4. Why does lather non give soap in hard h2o?
five. Why are synthetic detergents better than soaps?
Why should I download the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemical science Chapter 16 from BYJU'Due south?
Many students observe Chemistry as a tough subject as it includes derivations, concepts, structural formula and chemical reactions. The NCERT Solutions at BYJU'S provide students with a clear idea about the concepts which are important for the exam. The solutions completely adhere to the latest syllabus designed by the CBSE board. Students can download the PDF from BYJU'S and analyse the type of questions which tin can be asked in the board exams.
Source: https://byjus.com/ncert-solutions-class-12-chemistry/chapter-16-chemistry-in-everyday-life/
Postar um comentário for "Modern Chemistry Textbook Chapter 16 Chapter Review Answers Pdf"